Rajaji Tiger Reserve-Famous for Asian Elephant and Tigers
More than 50 species of mammals including the highly endangered Asian Elephant and Tiger found in the Park.
Besides tiger, leopard, Himalayan Black bear, sloth bear, Civet, Marten, Jackal, Hyena etc, it is estimated
that there are more than 350 Asian elephants in the park. Goral (Mountain Goat) - a characteristic mammals of the lower
Himalayas abound in the precipitous slopes of the Shivalik hills. Three species of deer - Sambhar, Spotted Deer
(Cheetal) and Barking Deer (Kakar) and animals like Wild Boar, Neel Gai. Langoor, Black Napped Hare, Jungle cat etc
are also found.
Over 300 species of birds are reported from Rajaji Tiger Reserve, making it an important birding area in the Country.
Of these, about 90 species are migrants, which include Pochards, Gulls, Mallards, Teals and Shellducks that
visit the water bodies of Bhimgora and Virbhadra Barrage and wetlands of river Ganga. The resident Birds include Pea Fowl, Jungle Fowl, different Parakeets, Woodpeckers, Kingfishers, Thrushes, Warblers, Barbets and Finches etc.
Great Pied Hornbill occupies a place of pride among the different Hornbills found in the Park.
Rajaji teems with wildlife. It harbours one of the most diverse ranges of wildlife habitats. Forests of Rajaji
include the Moist Shivalik Sal Forest, Moist Mixed Deciduous Forest, Northern Dry Mixed Deciduous and Khair-Sissoo
forests in the Southern Slopes, Low Alluviaval Savannah woodlands cover the drier southern margis of the Park.
The higher reaches of the Shivalik hills are swathered in Chir-Pine Forest.
Rajaji Tiger Reserve now become Rajaji Tiger Reserve dated on 20th April, 2015. Know More...
The Biodiversity of Rajaji

Rajaji Tiger Reserve is now has been finally notified as National Park status in September 2012. The two government prestigious wildlife conservation projects - The Project Elephant and The Project Tiger has now approved. It has got now all privileges and function of National Park
The Park itself is composed of three components: Rajaji founded in 1948; Motichur founded in 1936; and Chilla founded in 1977. They Spread over 820 sq. km. and were togethered named Rajaji Tiger Reserve in 1983
Rajaji Tiger Reserve is situated in the foothills of the Shivalik Range of Himalayas. Most of the land is covered by Sal forests.
A significant part of the Haridwar Range Reserve Forest runs contiguously with Chilla's southern and south-eastern boundaries. While this gives animals some extra space, it causes jurisdiction headaches, and the park authorities have set in motion a plan to attach Haridwar Forest in Rajaji.









 How to Reach Rajaji Tiger Reserve
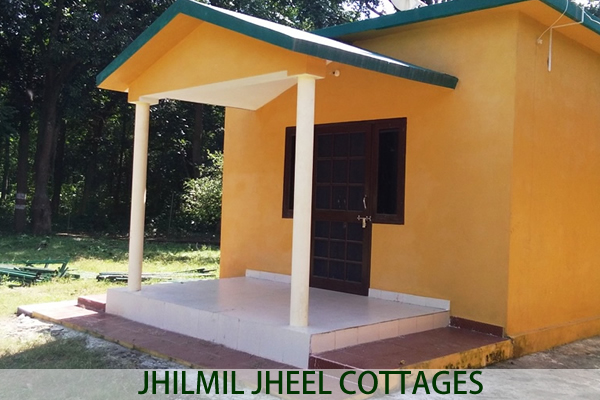
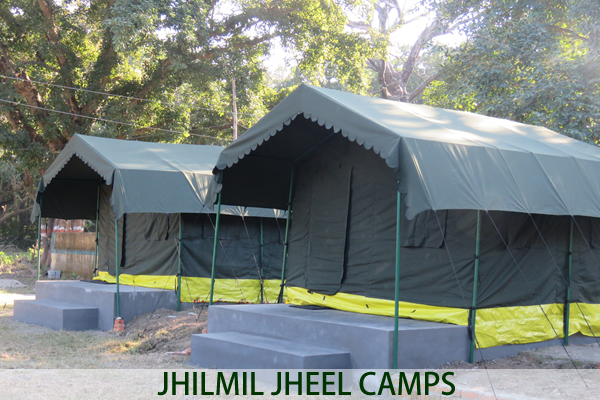
How to Reach Rajaji Tiger Reserve FRH and Resorts at Rajaji Tiger Reserve
FRH and Resorts at Rajaji Tiger Reserve Park Timings, Tickets and Entries
Park Timings, Tickets and Entries







